How Blockchain Operates: Step-by-Step Guide
Before learning how blockchain works, we have to know what blockchain is. Let’s first define blockchain. Fundamentally, a blockchain is a distributed ledger system that stores information on several computers in a manner that stops changes after it is made. It is not dependent on a central authority like traditional databases are.
To learn more about blockchain check Blockchain Technology: Discover Its Exciting World
Blockchain Operation: Step-by-Step Guide
The following steps provide a concise explanation of the intricate underlying blockchain mechanisms. The majority of these steps can be automated with blockchain software:
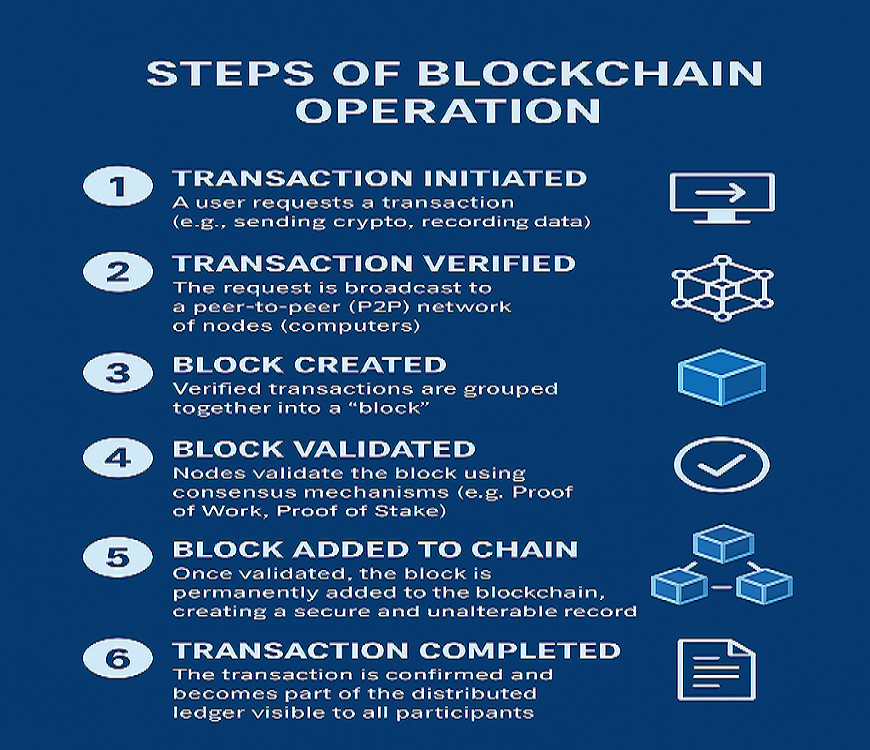
First, note the transaction.
The transfer of digital or tangible assets between parties within a blockchain network is depicted by a transaction. It is stored as a data block and may contain information such as this:
- Who took part in the deal?
- How did the transaction go?
- How long ago was the transaction completed
- What location was the transaction held at?
- What was the reason behind the transaction?
- What percentage of the asset was traded?
- How many prerequisites were satisfied in the course of the transaction?
Obtain agreement
On the distributed blockchain network, the majority of users must concur that the transaction that was recorded is legitimate. Although they can differ depending on the kind of network, norms of agreement are usually set up at early stages.
Connect the blocks
The blockchain records transactions in blocks, which are comparable to the pages of a ledger book, when the participants have come to an agreement. The new block is additionally added with a cryptographic hash in addition to the transactions. The blocks are connected by the hash, which functions as a chain. The hash value varies if the block’s contents are altered, whether on purpose or accidentally, offering a means of identifying data tampering.
As a result, you are unable to alter the blocks and chains and they link securely.
Because of this, the blocks and chains link securely and are unchangeable; each new block reinforces the verification of the previous block and, consequently, the blockchain as a whole; this is analogous to building a tower out of wooden blocks; you can only stack blocks on top of each other, and removing a block from the center of the tower causes the entire tower to collapse.
Share the ledger
The system sends out the most recent version of the central ledger to each participant.
For deeper technical detail, visit blackduck.com to learn how blockchain works
For instance:
Sending Bitcoin is an example of a transaction that is broadcast to every blockchain in the network. After receiving the transaction, each node verifies its validity using a consensus method like Proof of Work or Proof of Stake. The transaction is attached to a new block following validation. After that, the block is connected to the live blockchain. Changing one block would break the chain because each block carries a cryptographic hash of the one before it.
Why Is Blockchain So Safe?
By design, blockchain is safe. This is the reason:
- Data is transformed into an unreversible: fixed-length code using cryptographic hashing.
- Decentralization: The absence of a single point of failure.
- Transparency: In public blockchains, every transaction is visible on the public ledger.
- Consensus mechanisms: Prior to adding anything, make sure that all nodes agree.
- Related article: Blockchain versus Conventional Databases
Blockchain's Practical Uses
Blockchain is not limited to cryptocurrency. Typical uses include:
1-Smart contracts
contracts that run automatically using “if-then” reasoning and don’t require human involvement. These are made possible by platforms such as Ethereum.
2-Management of the Supply Chain
Monitor products from the point of origin to the point of delivery to maintain transparency and cut down on fraud.
3-Digital Identity
Verify asset ownership (NFTs, documents, etc.) and securely manage IDs with blockchain.
Limitations of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain isn’t perfect, despite its advantages:
- Problems with scalability in large transactions
- PoW systems’ energy usage
- Uncertainty in the law and regulations
Find out more at the World Economic Forum on Blockchain.
Conclusions
You now understand the entire blockchain process, from the start of a transaction to its eventual confirmation. It is one of the most inventive technologies available today because of its combination of decentralization, security, and transparency.
Continue reading on CryptoPulseUSA if you want to learn more about Web3, cryptocurrency investing, or DeFi tools